Linux File System Permissions and Advanced Commands For DevOps
Understanding Linux file permissions and ownership is crucial. We'll cover advance concepts, and commands.

Photo by Gabriel Heinzer on Unsplash
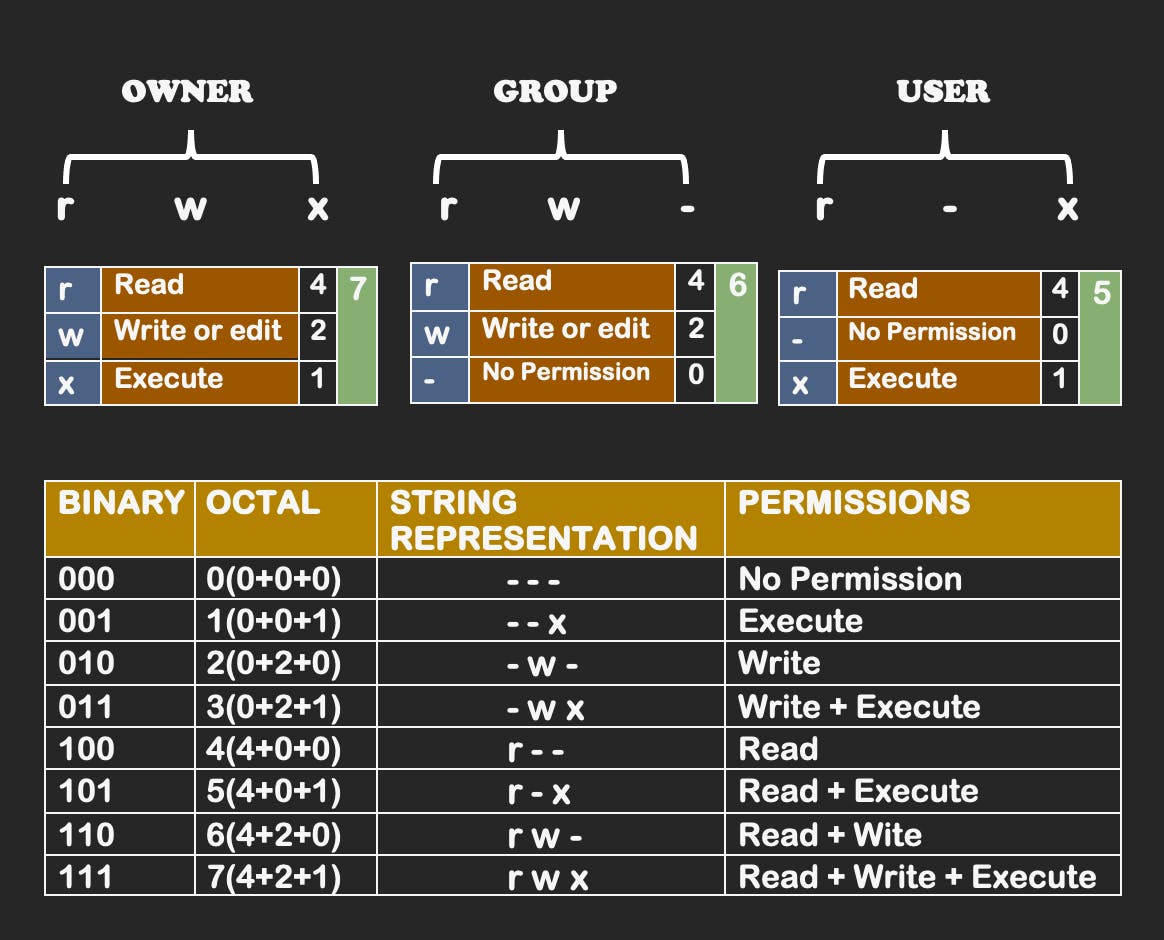
Linux File Permission
Linux file permissions use rwx triplets to control read, write, and execute access for the file owner, group, and all users, settable with chmod.
Types of File Permissions:
r (read): View file contents.
w (write): Modify the file.
x (execute): Allow or deny file execution.
Types of Permissions Groups:
User: File owner's read, write, execute access.
Group: Associated groups read, write, and execute access.
Other: All other users' read, write, and execute access.
File Permissions Commands:
How to check the number of users?
How to add a user?
How to add a group?

How to check the number of groups?
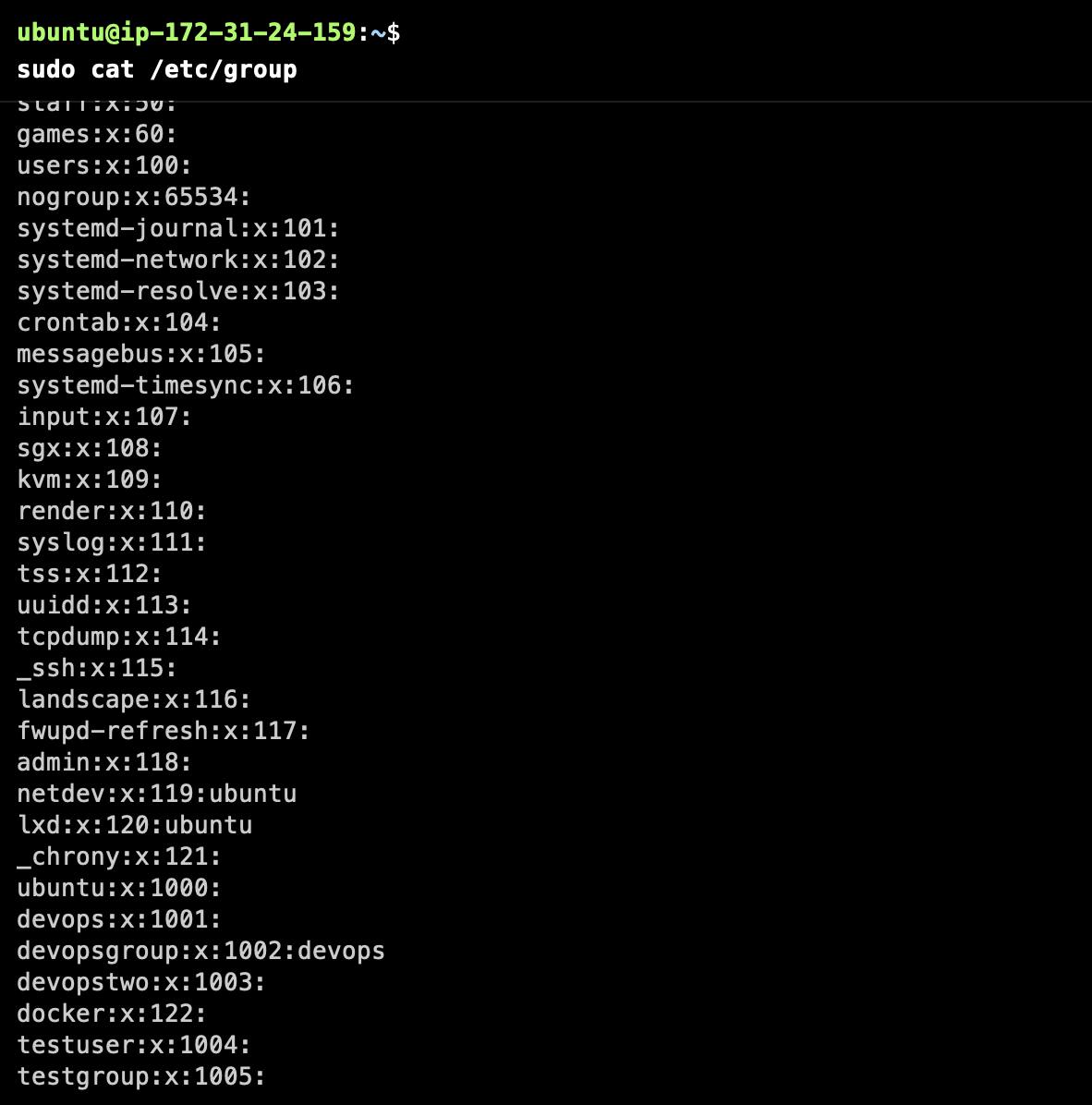
How to add a user to any group?

How to change a group of any file?
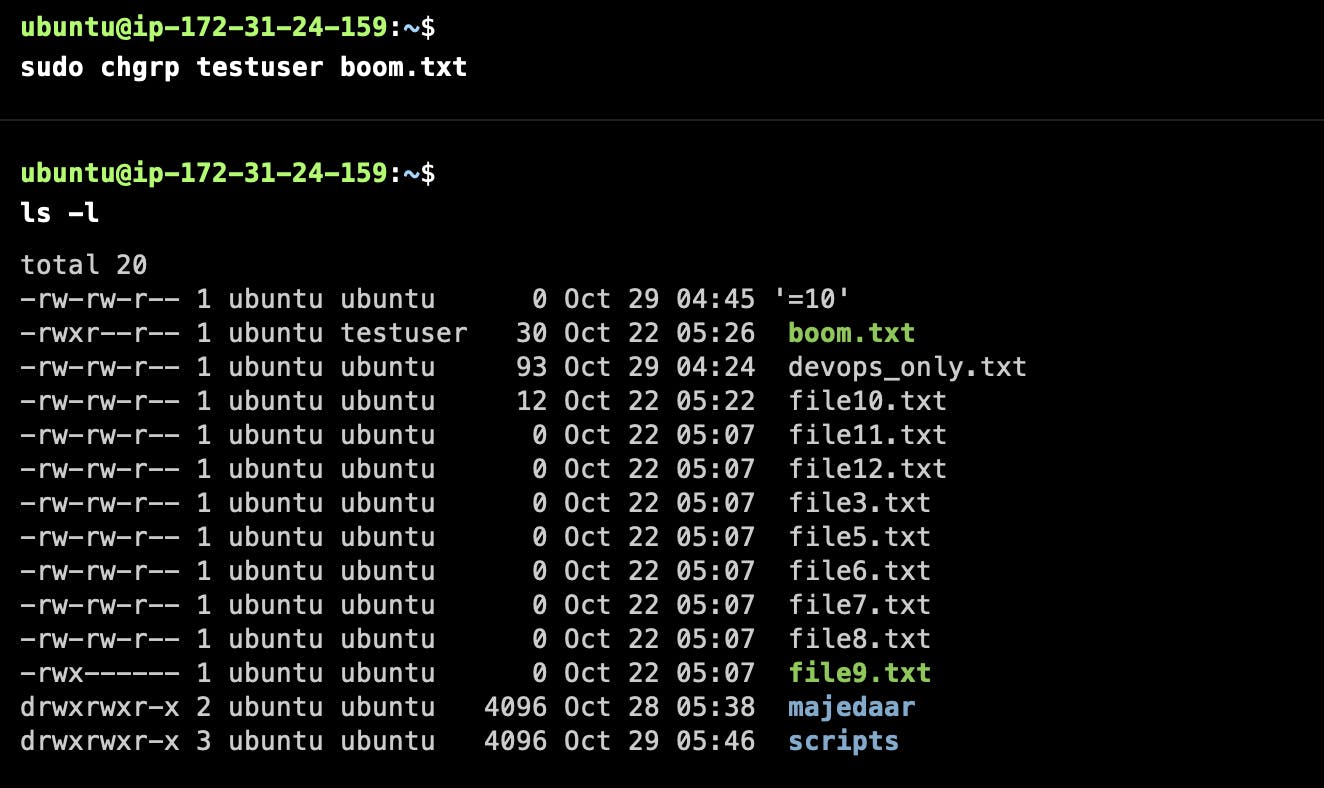
How to change the permission of any file?
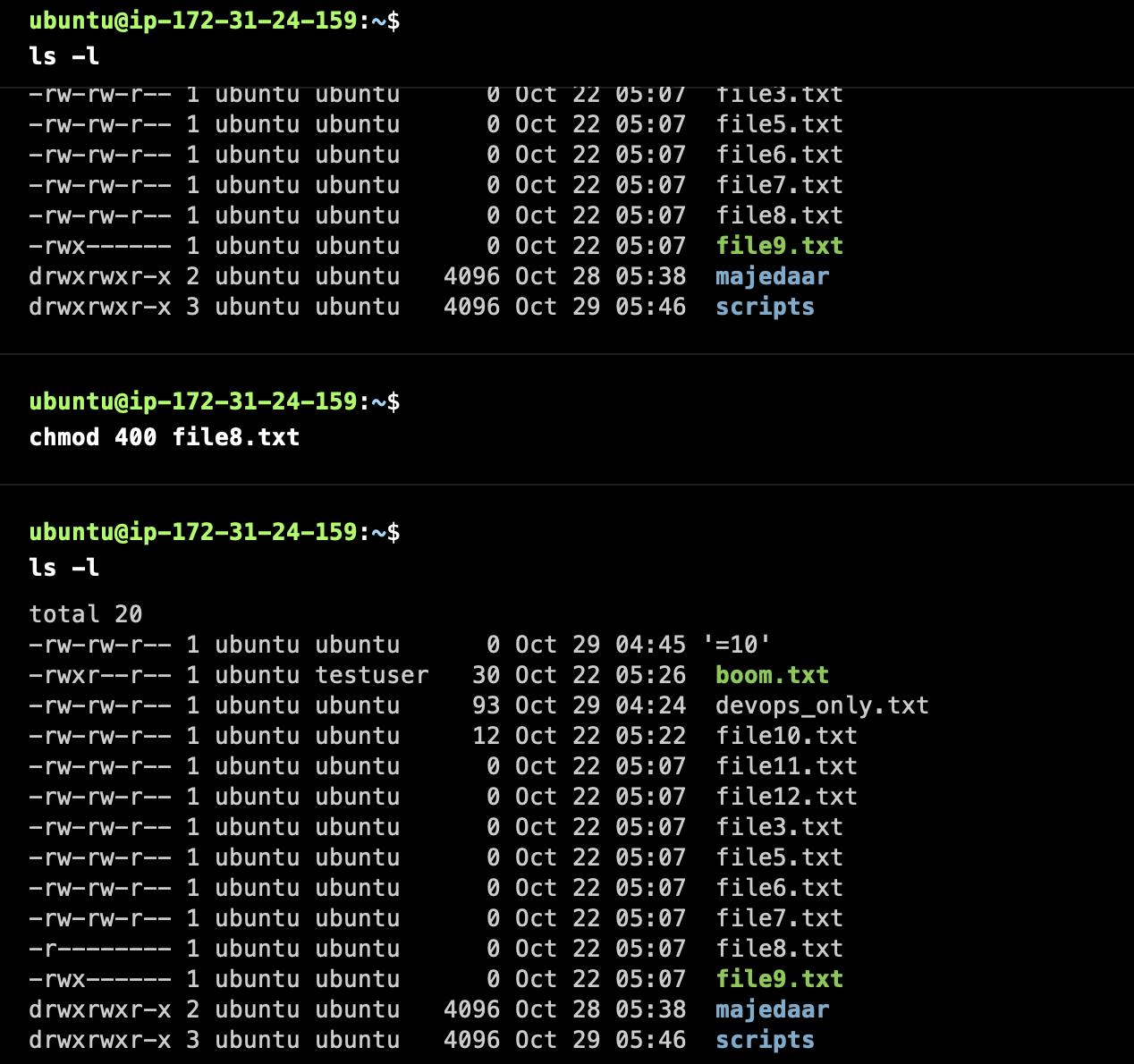
How to change the ownership of files and directories?
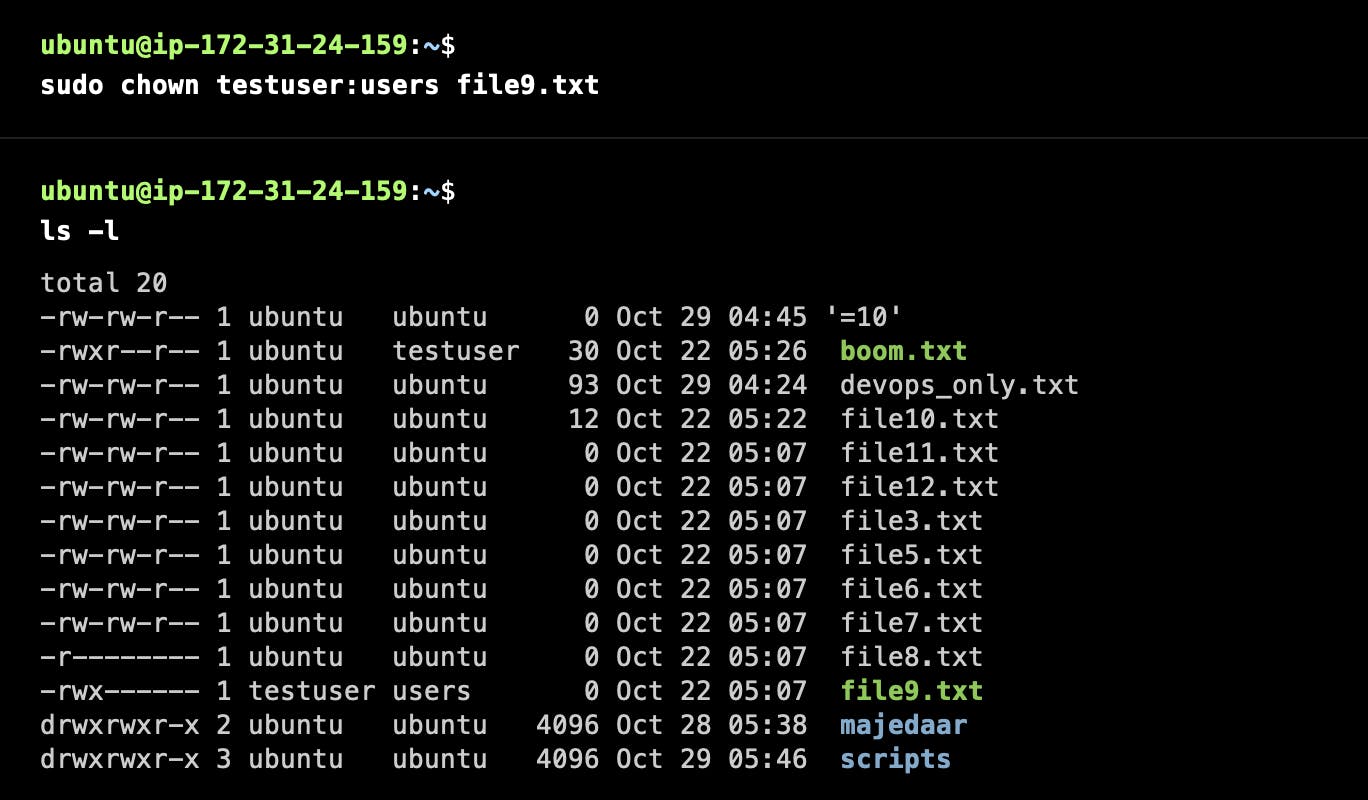
Other Important Commands:
scp
The 'scp' command in Linux is used for securely copying files between a local host and a remote host or between two remote hosts.
Local Host
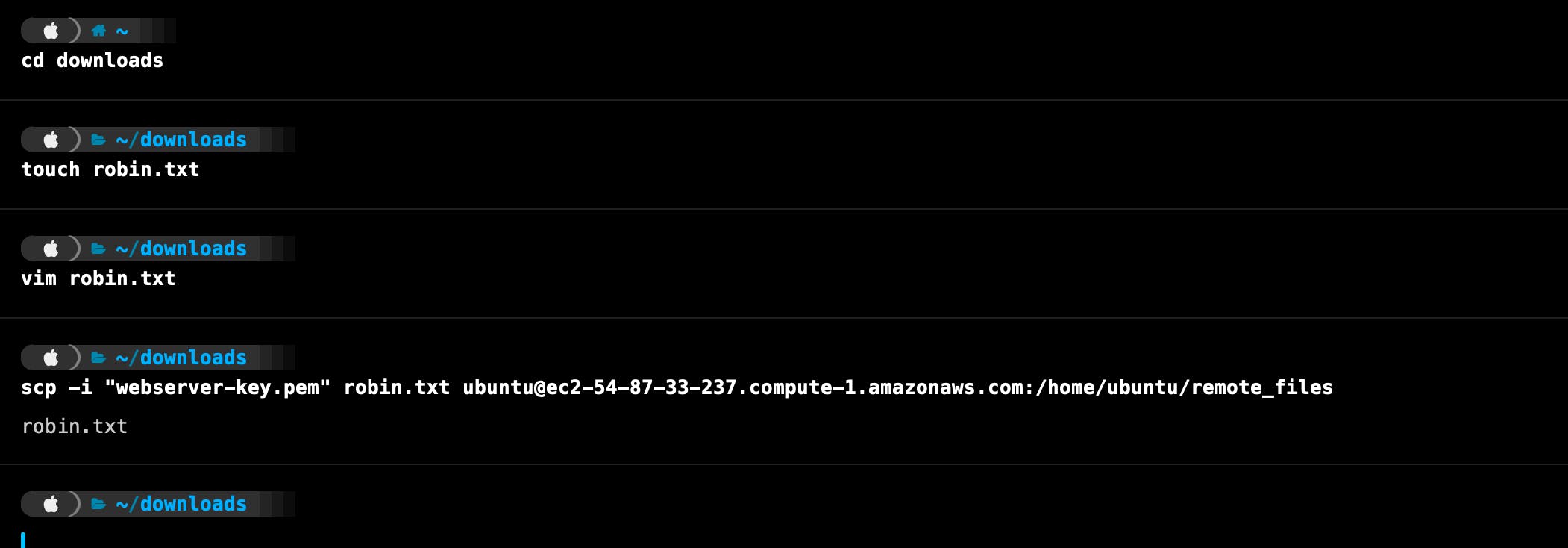
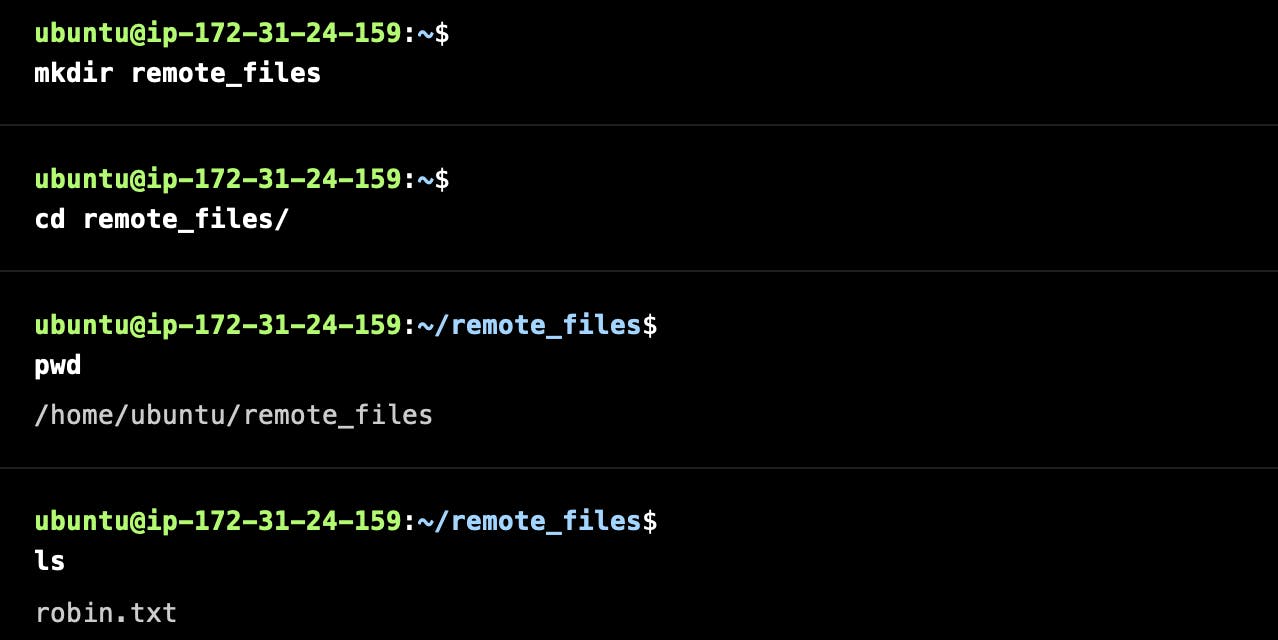
Remote Host
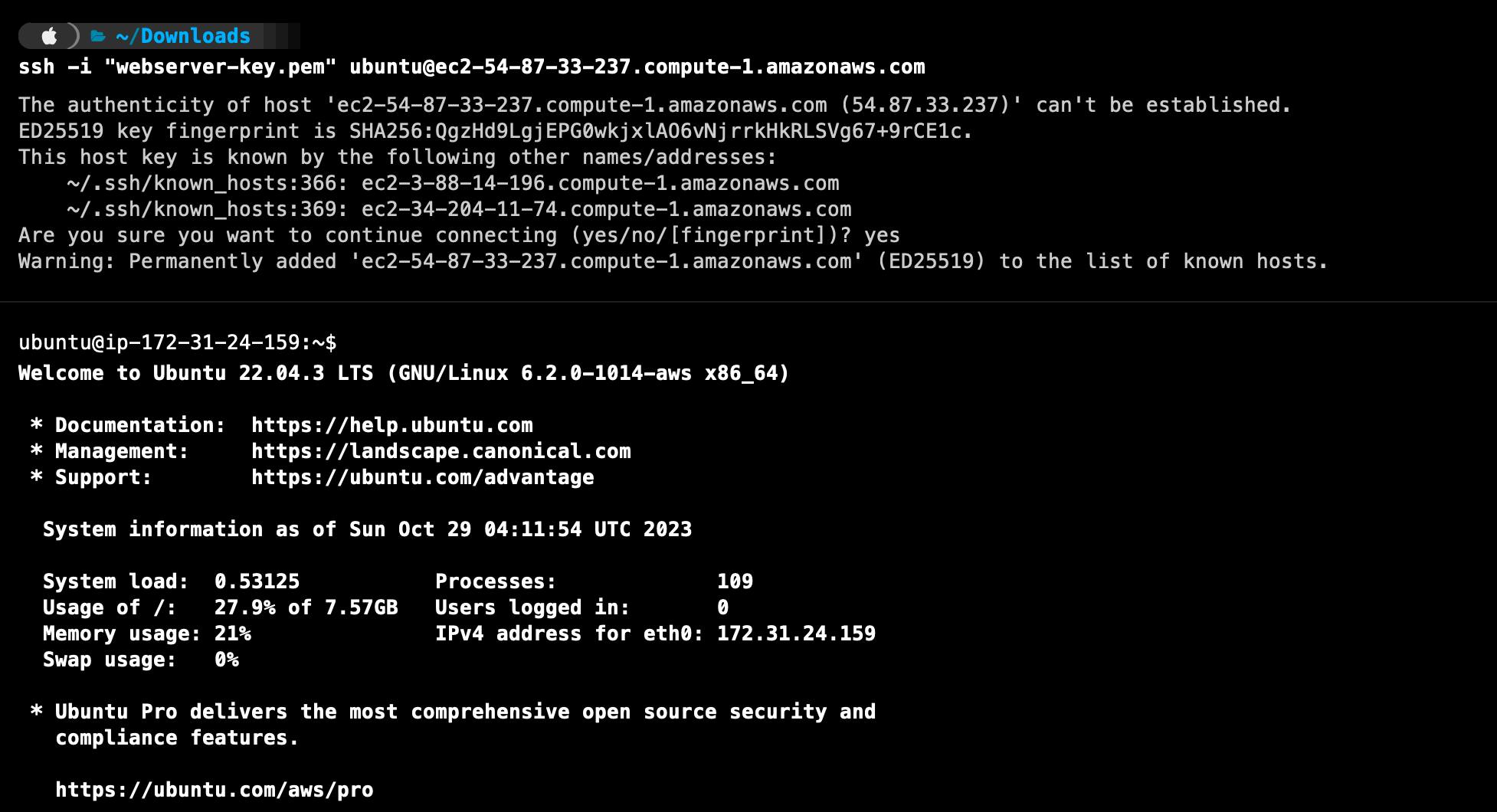
ssh
The 'ssh' command allows secure access to remote systems over an encrypted connection.
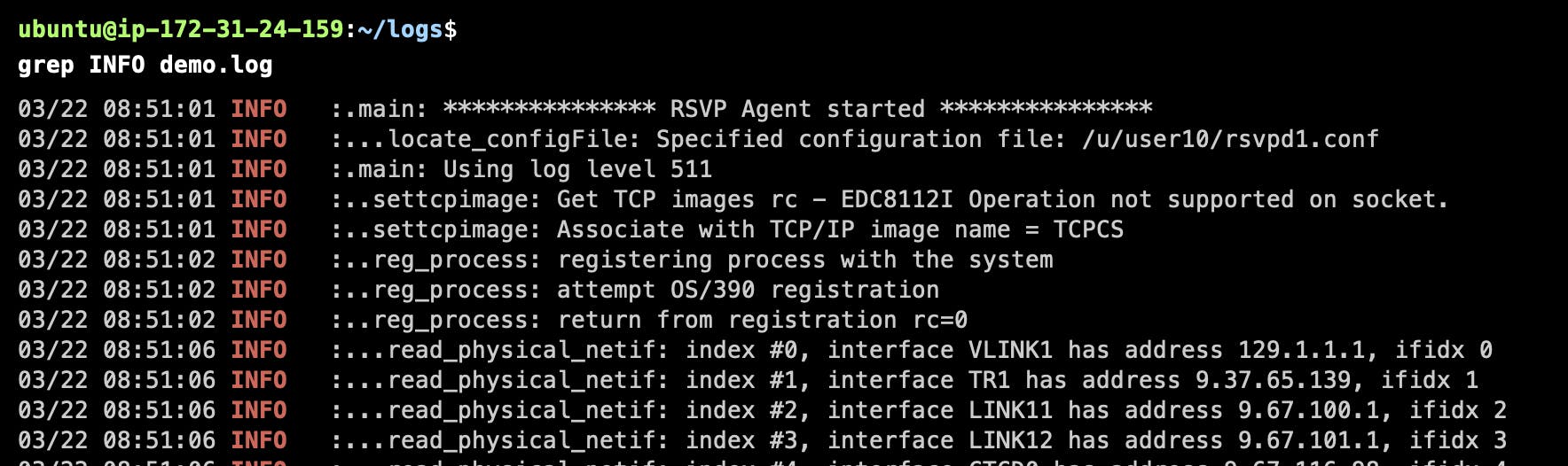
grep
The 'grep' command is used for searching and manipulating text.
Basic Text Search
Case-Insensitive Search
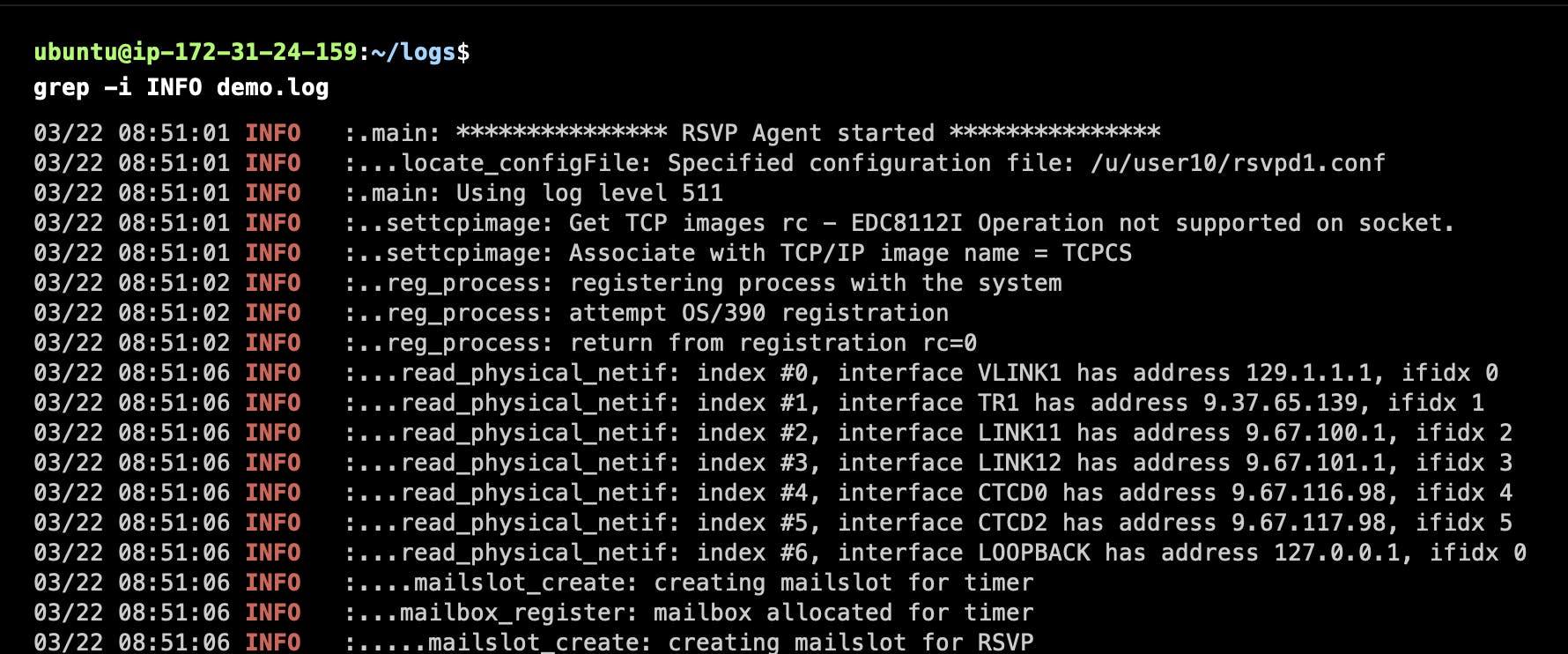
Display Line Numbers
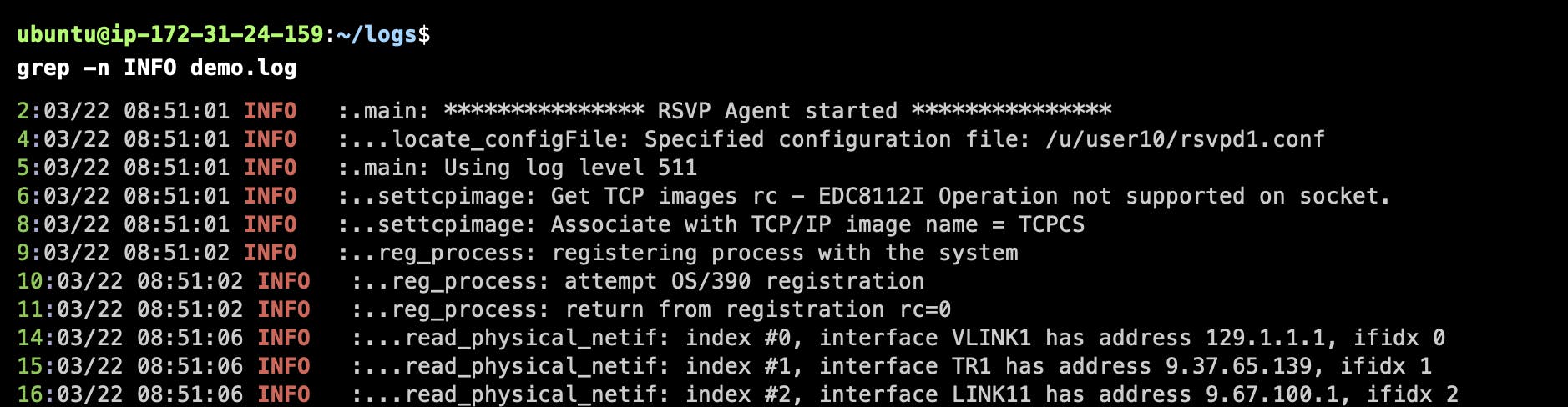
Count Matching Lines

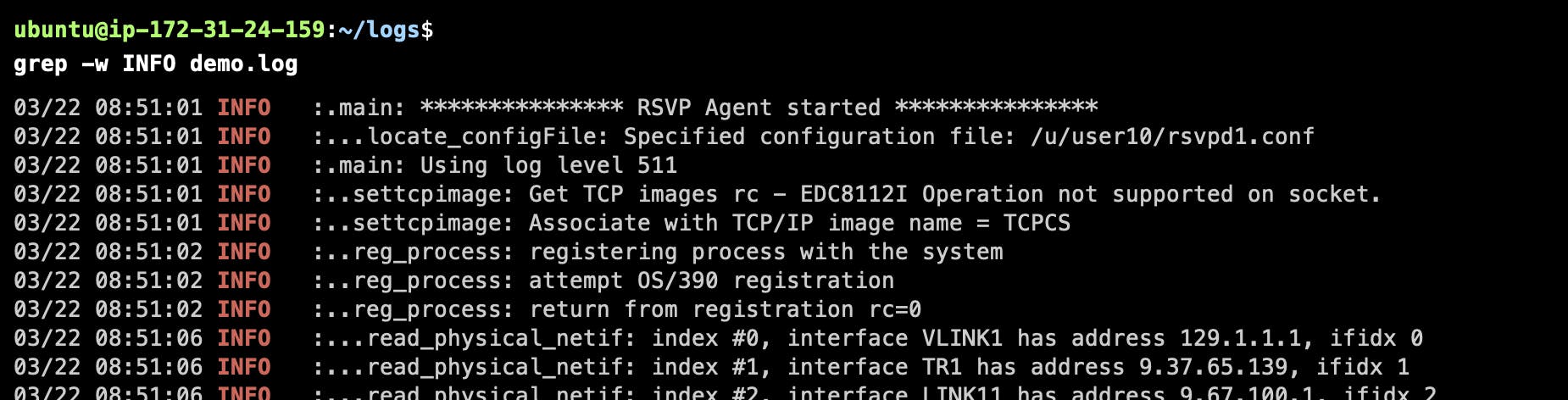
Search for Whole Words
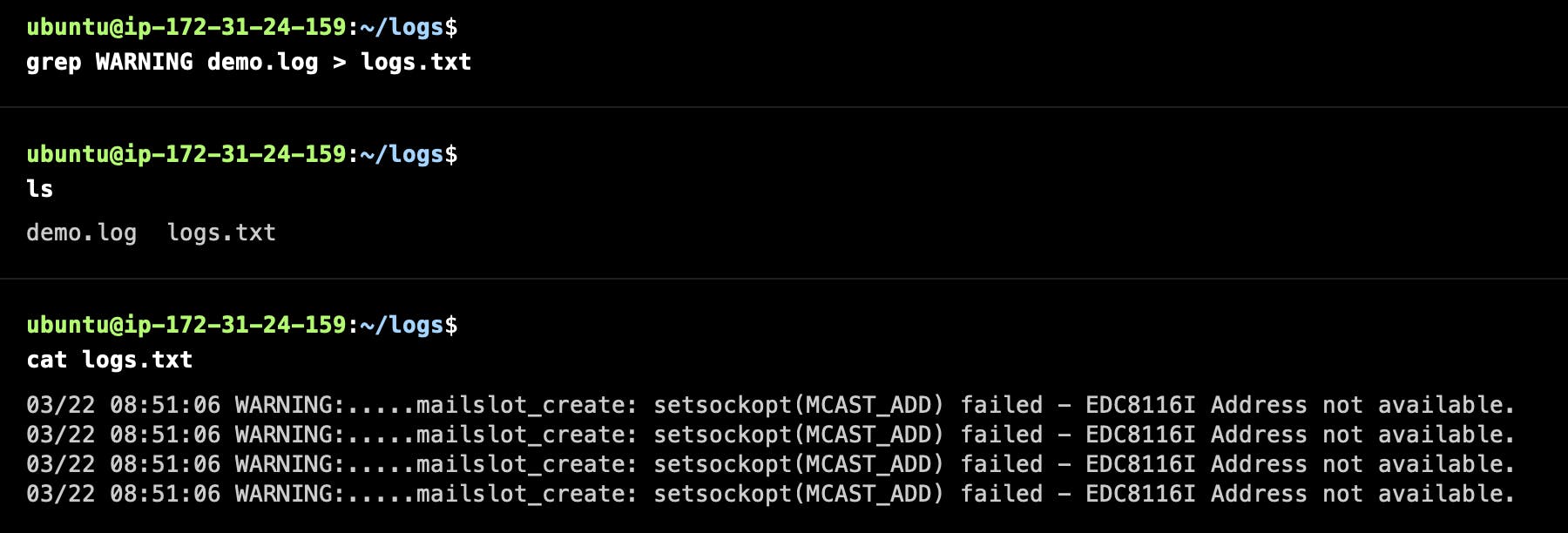
Search for lines containing the word and save it to another file
awk
The 'awk' command is used for pattern scanning, text extraction, reporting, and data analysis. It operates line by line, applying specified patterns and performing actions based on those patterns.
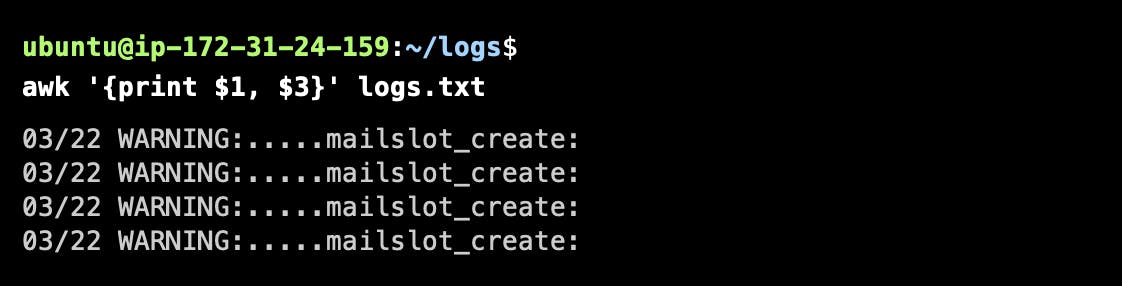
Print Specific Columns from a File
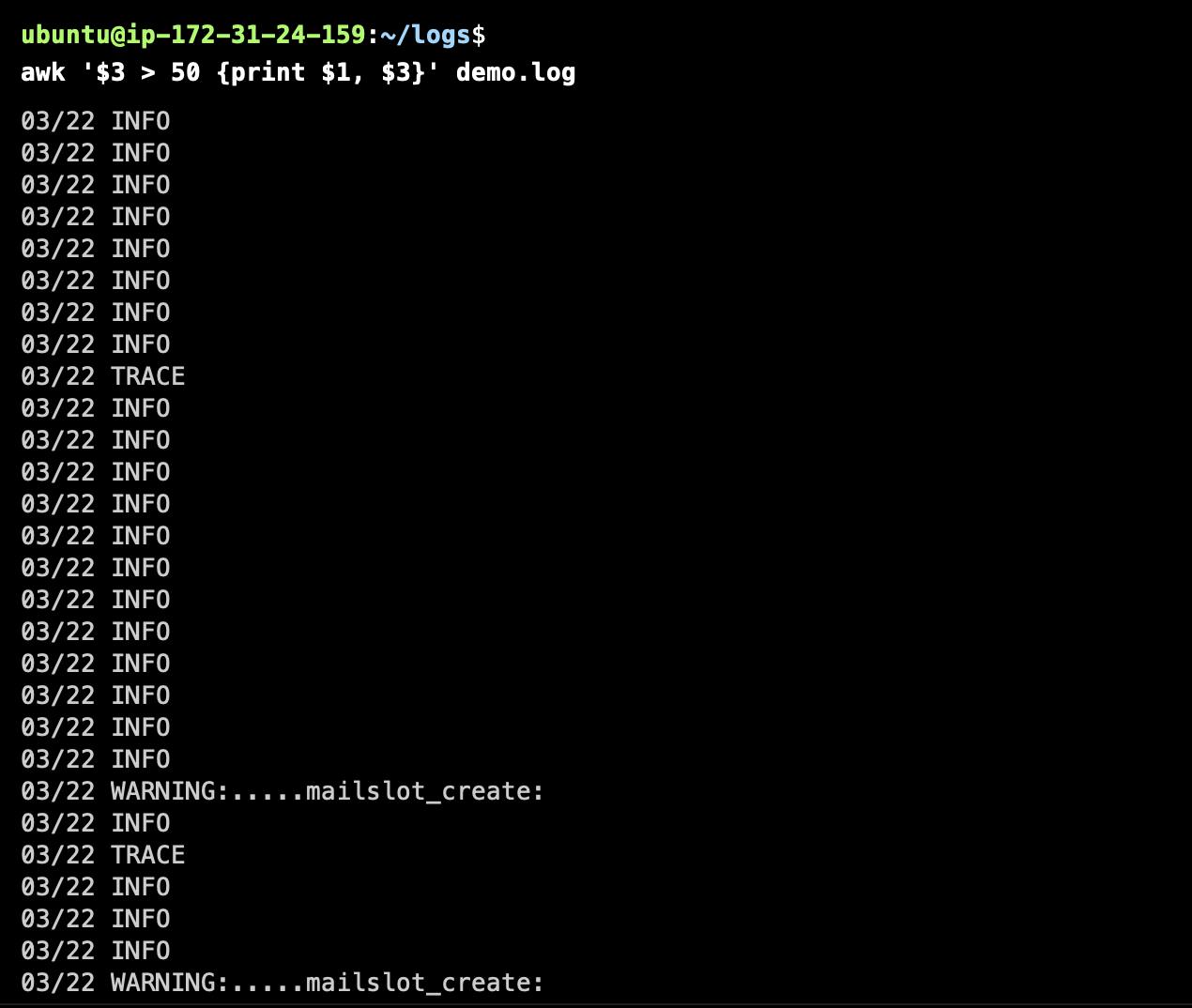
Conditional Printing
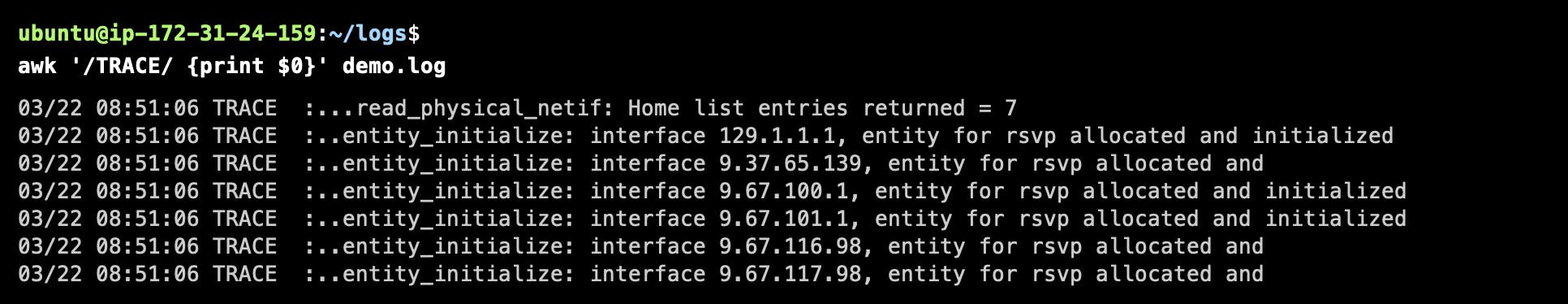
Pattern Matching
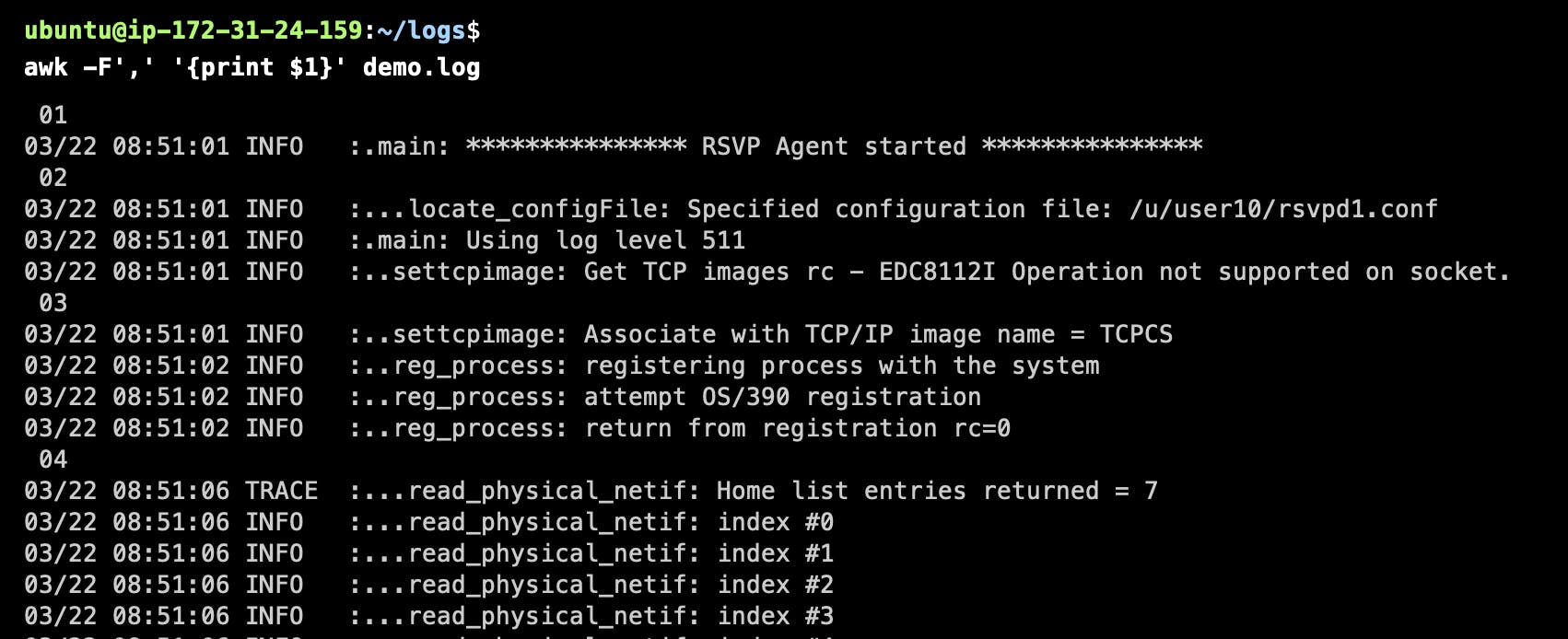
Field Separator
find
The 'find' command is used for locating files and directories based on various conditions.
Happy learning (^_^)